A Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) startup, DeepSeek, has emerged as a major disruptor in the global tech industry, sending shockwaves through U.S. markets and challenging the dominance of established players like OpenAI and Google. The company’s revolutionary AI model, R1, was developed at a fraction of the cost typically seen in the industry, marking a turning point in the global AI race. Here’s everything you need to know about DeepSeek, its innovations, and its impact on the global economy.
What is DeepSeek? A Low-Cost AI Revolution
DeepSeek, founded in 2023 by Chinese entrepreneur Liang Wenfeng, has quickly emerged as a formidable player in the AI sector. Based in Hangzhou, China, the startup introduced the R1 model, a ChatGPT-like AI system developed for a mere $5.6 million. This cost is a fraction of the billions spent by U.S. giants like OpenAI, Google, and Meta on similar AI technologies.
What sets DeepSeek apart is its efficiency. Utilizing a mix of advanced engineering techniques and a combination of high-performance and low-power chips, the DeepSeek model delivers comparable performance to Western models like OpenAI’s GPT series. Liang’s team of young PhD graduates from top Chinese universities employed novel architectures, such as Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) and Mixture-of-Experts, to achieve these results.
DeepSeek Sends U.S. Tech Stocks Tumbling
DeepSeek’s debut has spooked Wall Street, with major U.S. tech stocks taking a hit. Nvidia stock (NVDA), known for its dominance in AI chips, fell by 12% in premarket trading. Other tech giants like Meta (META), Alphabet (GOOGL), and chipmakers like Marvell and Broadcom also experienced sharp declines.
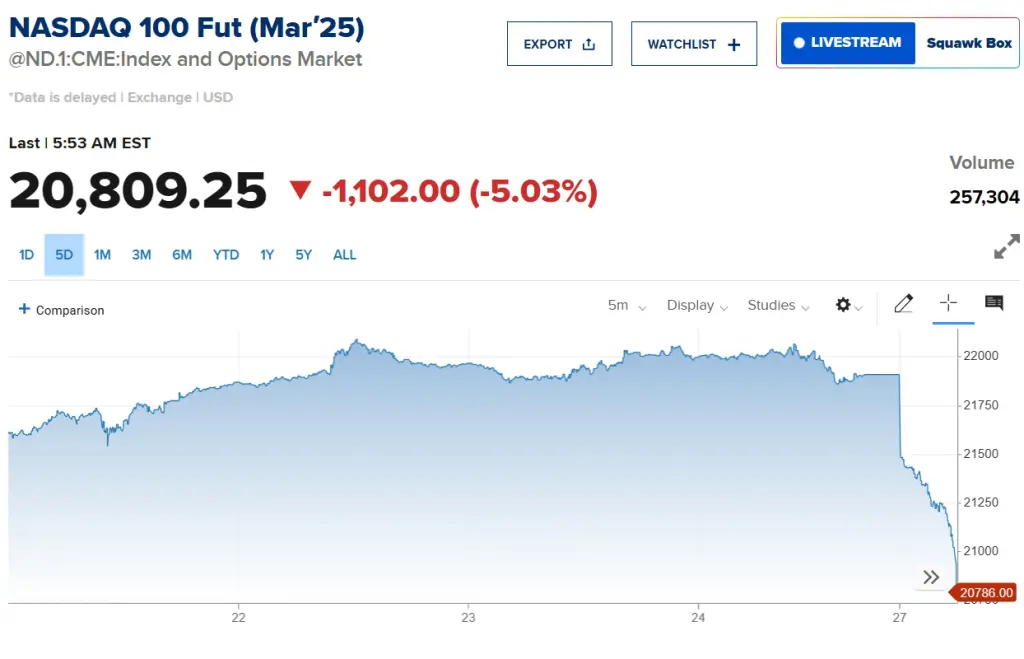
The S&P 500, with tech comprising about 45% of its value, dropped 2.4% at the market open, while the Nasdaq fell by 4.2%. Investors are now questioning whether the massive investments made by U.S. companies in AI infrastructure will yield expected returns.
Market analysts, including Keith Lerner of Truist, note that this is a wake-up call for U.S. tech. “The DeepSeek model rollout challenges the perceived lead that U.S. companies have in AI,” said Lerner.
DeepSeek Nvidia Partnership: How Chinese AI Beat the Odds
Despite U.S. export restrictions on advanced chips like Nvidia’s H100, DeepSeek Nvidia synergy became a reality thanks to Liang’s strategic planning. By stockpiling an estimated 50,000 Nvidia A100 chips before export bans took effect, DeepSeek optimized its hardware use to create a high-performing AI model on a limited budget.
Experts like Marina Zhang from the University of Technology Sydney believe that DeepSeek’s focus on software-driven resource optimization, rather than heavy reliance on hardware, has set it apart. This approach could become a blueprint for future AI developments globally.
AI DeepSeek Challenges Power Projections
DeepSeek’s efficiency isn’t just affecting tech stocks. U.S. energy companies like Constellation Energy, Vistra Corp., and GE Vernova, which have benefited from AI-driven demand for electricity, saw their stocks tumble. Investors are now questioning whether AI data centers will require as much power as previously forecast.
For example, Constellation had signed deals to power Microsoft’s AI data centers, while Vistra and Talen Energy were exploring similar projects. DeepSeek’s low-cost AI model raises doubts about these long-term energy demand assumptions, which had been driving the stock prices of power companies.
What Does DeepSeek Mean for the Global AI Race?
DeepSeek’s emergence could signal the beginning of a major shift in the AI landscape. By demonstrating that cutting-edge AI models can be developed at a fraction of the cost, DeepSeek challenges the dominance of Western tech giants.
Some view DeepSeek as “AI’s Sputnik moment,” a term used by Silicon Valley investor Marc Andreessen to liken the development to the Soviet Union’s surprise satellite launch in 1957. However, skepticism remains about whether DeepSeek can sustain its momentum and compete in markets dominated by U.S. firms.
Despite its achievements, Chinese AI companies like DeepSeek face hurdles, including reliance on less-advanced chips and geopolitical tensions. Nonetheless, the open-source nature of DeepSeek’s R1 model has earned praise within the global AI community and could accelerate innovation.
As the dust settles from DeepSeek’s stunning debut, the global tech industry is left grappling with the implications. Will U.S. firms respond with more efficient AI models, or will DeepSeek AI gain a foothold in the global market?


