What is E. Coli?
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, is a bacteria that lives in the intestines of humans and animals. While most strains are harmless, some, like the one involved in the McDonald’s outbreak, produce toxins that can cause severe food poisoning. Symptoms typically appear within 1-2 days of consuming contaminated food and include:
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea (often bloody)
- Dehydration
In severe cases, particularly in children under five, E. coli infections can lead to kidney failure, requiring immediate medical attention. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the bacteria causes approximately 74,000 infections and 61 deaths annually in the U.S.
McDonald’s E. Coli Outbreak: Key Facts
The outbreak has been traced to slivered onions used on McDonald’s Quarter Pounders. Investigations by the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) revealed:
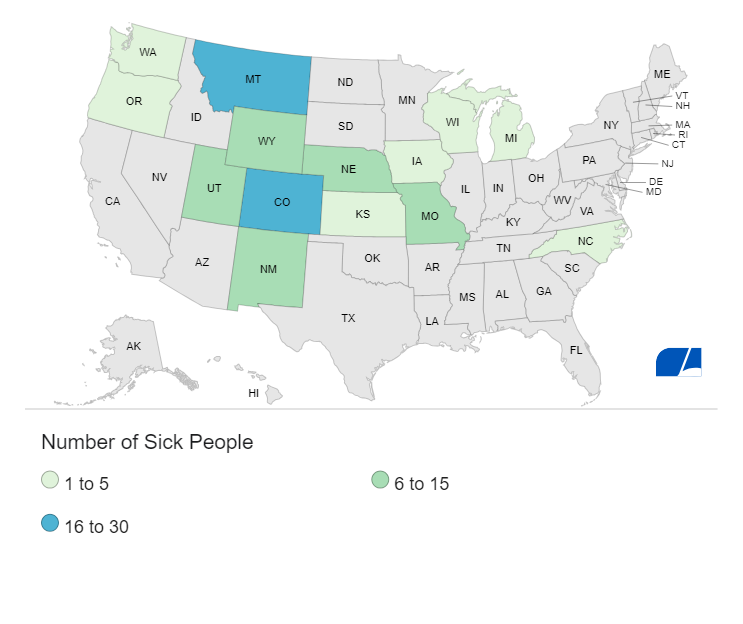
- 104 cases of illness across 14 states.
- 37 hospitalizations and 1 death in Colorado.
- Illnesses reported between September 12 and October 21, with many cases linked to McDonald’s menu items.
Taylor Farms, the supplier of the implicated onions, recalled potentially contaminated batches. However, FDA tests found that the bacteria strain in the onions did not fully match the one causing the illnesses.
McDonald’s Response and Recovery Efforts
To address the crisis, McDonald’s is investing $100 million, according to internal McDonald’s memo and obtained by CNN, in recovery measures, including:
1. Support for Franchisees
- $65 million is being directed to franchise owners in the hardest-hit states. This includes financial relief through rent and royalty deferrals.
2. Marketing Campaigns
- A $35 million marketing push promotes value deals, such as a 10-piece McNuggets deal for $1 through the app.
- Television ads emphasize the return of the Quarter Pounder, which is now available nationwide.
3. Menu Adjustments
During the outbreak, Quarter Pounders were removed from menus in affected areas, and an alternative onion supplier was identified. McDonald’s has since reintroduced the menu item, reassuring customers that rigorous food safety protocols are in place.
4. Communication and Transparency
McDonald’s executives, including CEO Chris Kempczinski, emphasized the company’s commitment to doing “the right thing” and providing a safe dining experience.
Impact on McDonald’s Business
The outbreak significantly affected McDonald’s sales and reputation:
- Foot traffic and sales declined nearly 12% in late October, according to Bloomberg.
- Share prices dropped approximately 7%, erasing much of the company’s year-to-date gains.
Despite these setbacks, McDonald’s executives remain optimistic, citing a gradual recovery in customer visits and loyalty.
Lessons from the Outbreak
The McDonald’s E. coli outbreak underscores the importance of stringent food safety measures in the fast-food industry. While the company has taken significant steps to address the situation, public trust will take time to rebuild.
For customers, understanding what is E. coli and its risks can help them make informed dining choices. For McDonald’s, this incident serves as a reminder of the critical need for robust supplier monitoring and transparency to prevent similar crises in the future.


