President Donald Trump has announced a significant agreement between the United States and Vietnam trade deal, marking a pivotal moment in U.S.Vietnam relations. The deal introduces a 20% tariff on Vietnamese imports to the U.S. and offers American goods tariff-free access to Vietnam’s markets.
Key Terms of The U.S.-Vietnam Trade Deal
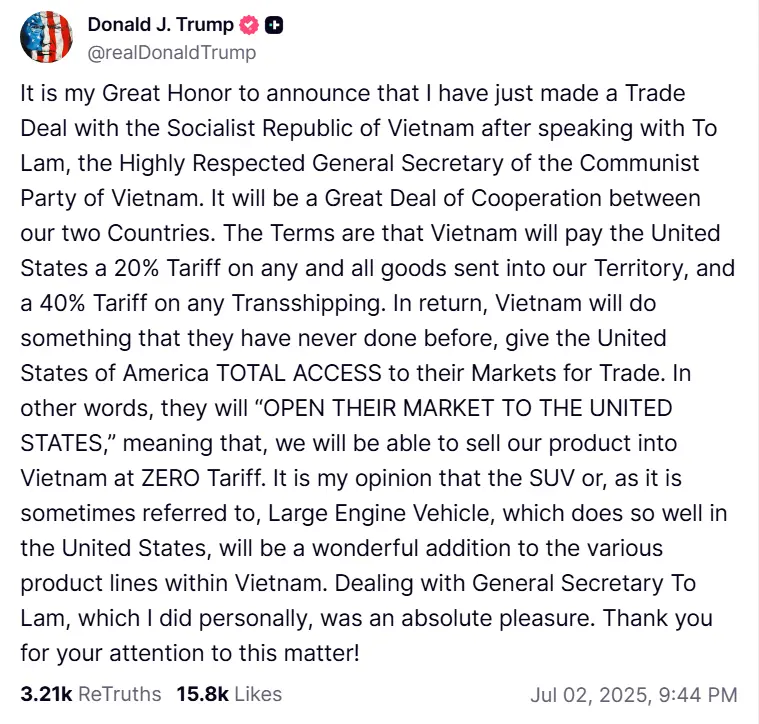
1. 20% Tariff on Vietnamese Imports
Under the new agreement, Vietnamese goods entering the U.S. will be subject to a 20% tariff. This rate is a reduction from the previously proposed 46% tariff, reflecting the outcomes of extensive negotiations between the two nations.
2. 40% Tariff on Transshipped Goods
To combat the practice of transshipment, where goods from third countries are routed through Vietnam to circumvent tariffs, the agreement imposes a 40% tariff on such products entering the U.S. This measure aims to ensure that only goods genuinely produced in Vietnam benefit from the reduced tariff rates. axios.com
3. Zero-Tariff Access for U.S. Goods to Vietnam
In exchange for the tariffs on Vietnamese imports, Vietnam has agreed to grant U.S. goods zero-tariff access to its markets. This provision is expected to open new opportunities for American exporters, particularly in sectors like automotive and agricultural products.
Strategic Implications
Economic Impact
The agreement is anticipated to have a significant impact on both economies. For the U.S., the reduced tariffs on Vietnamese goods may lead to lower import costs, benefiting consumers and businesses reliant on these imports. Conversely, the zero-tariff access to Vietnam’s market could boost American exports, supporting sectors such as agriculture, technology, and manufacturing.
Geopolitical Considerations
This deal also carries geopolitical weight. By strengthening economic ties with Vietnam, the U.S. may be aiming to counter China’s influence in the region. The agreement could serve as part of a broader strategy to diversify trade partnerships in Asia.
Vietnam and U.S. Industry Reacts
Automotive Sector
The automotive industry, particularly manufacturers of large engine vehicles like SUVs, stands to benefit from the agreement. President Trump highlighted the potential for American SUVs to gain popularity in Vietnam, a market that has traditionally been less receptive to such vehicles.
Textile and Electronics Industries
Vietnam is a major exporter of textiles and electronics. The new tariff structure aims to ensure that these goods are genuinely produced in Vietnam, potentially reshaping supply chains and encouraging more localized production.
Vietnam has become a major manufacturing hub due to rising labor costs in China and companies seeking to diversify their supply chains—known as “friend-shoring.” The previous U.S. tariffs on Vietnamese trade threatened to disrupt these adjustments, but the new agreement helps preserve Southeast Asian production strategies.
This new U.S.-Vietnam trade deal represents a significant development in international trade relations. By imposing a 20% tariff on Vietnamese imports and granting zero-tariff access to U.S. goods, the deal seeks to balance trade imbalances and foster economic cooperation between the two nations. As the agreement is implemented, its long-term effects on trade patterns and economic growth will become more apparent.
For global supply chains, the enforcement of non-transshipment rules is crucial. The 40% tariff serves as deterrent against companies misusing Vietnam as a conduit for goods intended for the U.S. market.


